Login & Startpage
Login and password
Structure of SmartProcess
Customize start page
Elements on the start page
Customize main menu
Full text search
Workflows and Cases
Create Workflows
Workflow objects
Workflow object: Task
Workflow object: Decision
Workflow object: Forward case
Workflow object: Send e-mail
Workflow object: Start, intermediate and end event
Workflow object: Timer
Workflow object: Parallel gateway
Workflow object: Sub-Process
Workflow object: Incoming message
Workflow object: Send form via e-mail
Workflow object: Service/Export
Form designer
Form fields
General field properties
Field: Text / List without multiple selection
Field: Multiple selection list
Field: Multirow text
Field: Multirow formatable text
Field: Number
Field: Date
Field: Date / Time
Field: Function-Fied
Field: Contact selection
Field: Field group
Field: Catalog fields
Field: Data source for processes and documents
Field: Process and Document fields
Field: Wiki
Field: Free input
The form designer
Workflow basics
Process model of a workflow
Workflow Settings
Rights workflow participants
General placeholders for Word reports in workflows
Case processing
Workflow-Applications
Processes
Menu structure & terms
Process modelling
Process objects
Overview: BPMN objects
Object: Task
Object: Sub-Process
Object: Connectors
Object: Events
Object: Gateways
Object: Pool & Swimlane
Object: Artifacts in general
Object: Artifacts IT System, Resource
Object: Data object Input / Output, Adjacent process
Object: Artifacts KPI, Risk, Control, Opportunity
Object: Artifact Related document
Additional modelling objects
User-defined images as modeling objects
The process designer
Create process groups & processes
Formatting and positioning objects
Reuse & copy objects
Process details
List: Details
User-defined fields
List: Actions
List: Documents
Lists: Terms and abbreviations / Requirements
Lists: Indicator (KPI), Risks, Opportunities
List: Process participants
Process description
Publication and access rights
State and version
Publication of processes / documents
Validity
Read and edit access
Read confirmation
Knowledge questions for read confirmation
Additional features for processes
Documents
Documents - menu structure
Create documents
Document details
Edit files directly in Office
Properties and Placeholders in Word files
Documents - State, version, publication and validity
Organization chart
Reporting
Reporting menu
Reporting for processes and documents
Reporting for cases
Saved reports
Share reports
Excel Report Designer (Additional module)
Catalogs
Settings
Users, permissions & organizational units
Authorization profiles
Introduction authorization profiles
Authorization profile - Tab Workflows / Cases
Authorization profile - Tab Processes
Authorization profile - Tab Documents
Authorization profile - Tab Organization chart
Authorization profile - Tab Reporting
Authorization profile - Tab Contact
Authorization profile - Tab User
Authorization profile - Tab Catalogs
Authorization profile - Tab Wiki
Authorization profile - Tab Administration
Authorization profile - Tab Others
Organizational units and roles
Manage users
Representative
Catalogs
Import
Import of data
Contact import
User import
Organizational unit import
Case import
Meta data import for documents
Emails and text modules
Configure application
Language
Automatic translation
Date and time
Login options and views
Settings for process management
Modeling rules
Symbols for processes and process groups
Process view
Settings for document management
Document templates
Document type
Settings for the organizational chart
Display of the logos
Unavailability for cases for dates
Directory services (AD, Entra ID / Azure AD) and single sign-on
User notifications
Password security
IP Filter (only for SaaS Systems)
API Profile (Additional module)
Manage maintenance access (only for SaaS systems)
Word report designer for printouts (Additional module)
AI Function SmartAI (Additional module)
Audit Trail
Initial configuration SmartProcess - Process and document management
Video tutorials
Video tutorials: Business Process Management
Video tutorial for process participants
Video tutorial for working with workflow cases
Video tutorial on audit management
Version & Release notes
Release Notes
Version 24.9 Release Notes
Version 23.10 Release Notes
Version 22.10 Release Notes
Version 22.5 Release Notes
Version 22.3 Release Notes
Version 21.3 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.10 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.9 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.8 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.7 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.6 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.5 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.4 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.3 Release Notes
Manuals from previous versions
Version 25.11 Release Notes
Version 25.3 Release Notes
Info about version
General
SmartProcess API
Mobile Web App
HTML field
Contacts
File attachments in SmartProcess
Manage Wikis
Use QR codes with SmartProcess
Contact & Forum
Table of Contents
- All Categories
- Processes
- Process modelling
- Process objects
- Object: Task
Object: Task
A task is a self-contained sub-step of a process. During modeling in the Process Designer, a double-click on a task icon opens its properties. Task details. Window Properties Description / Details Vi…

A task is a self-contained sub-step of a process. During modeling in the Process Designer, a double-click on a task icon opens its properties.
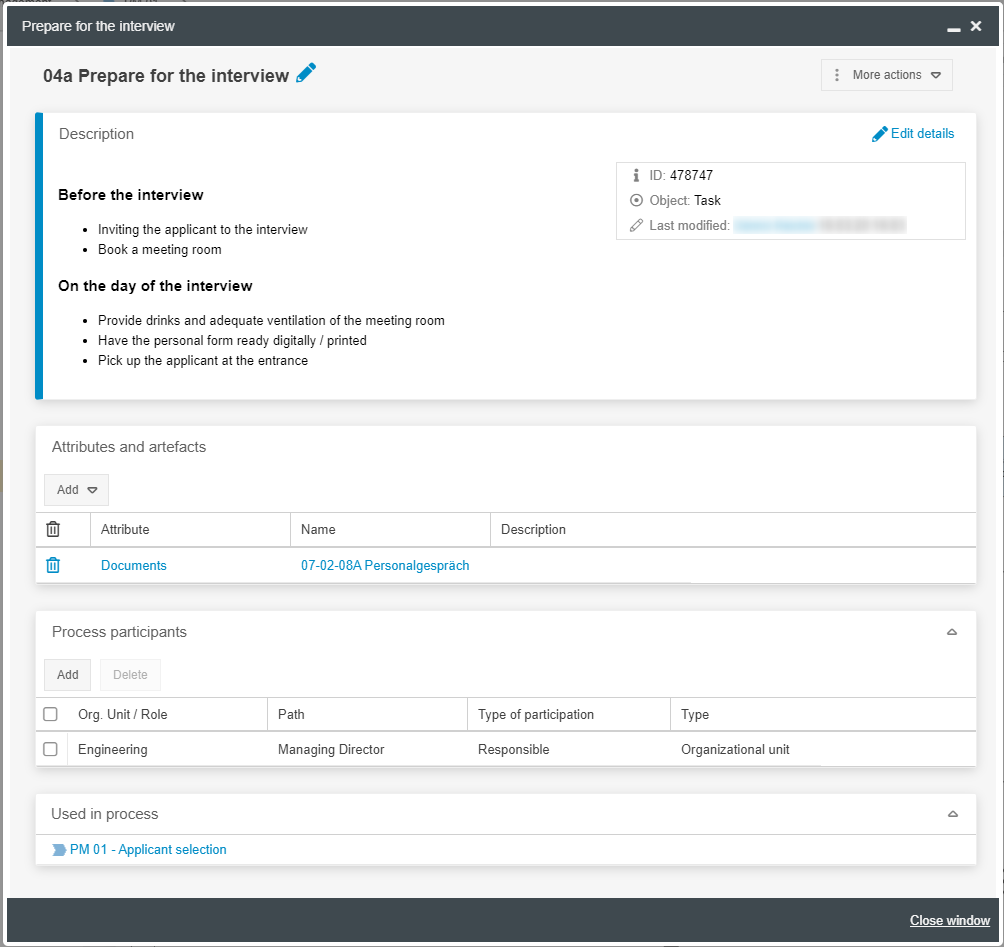
Task details
Window | Properties |
Description / Details | Via <Edit details> the name and numbering of the task can be changed. A detailed task description including images and links can be entered in an HTML text field. The small  icon in the upper right corner of the task icon shows that a task description has been entered. icon in the upper right corner of the task icon shows that a task description has been entered.The defined numbering is visible at the bottom left of the task icon. 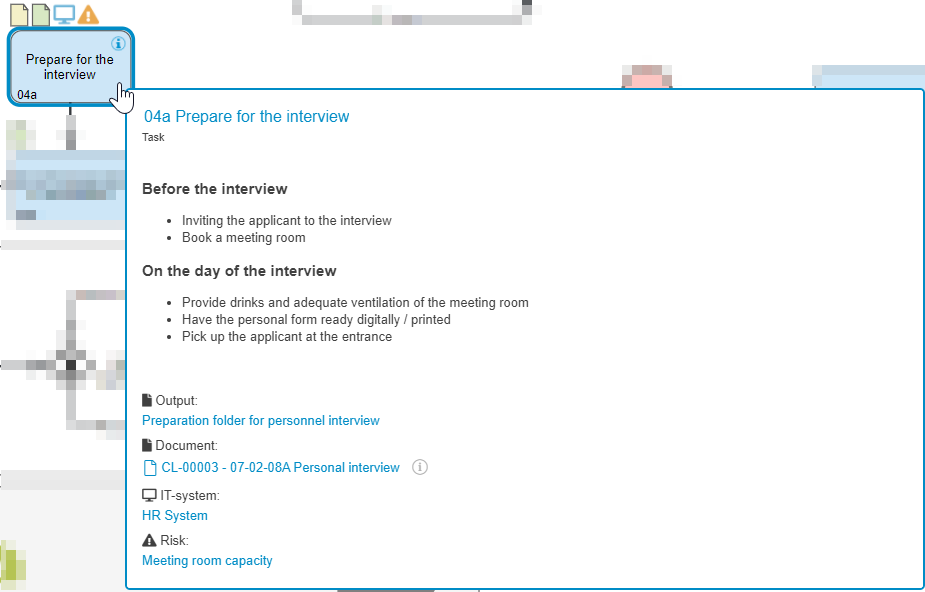 If the user points at a task with the mouse in the read-only view of the process, the description and artifacts linked to the task are shown without clicking on the task. |
Attributes and artifacts | With <Add> in the Attributes and Artifacts area, various artifacts can be linked to the task. Which artifacts were linked to which task is also visible in the PDF template process description. |
Process participants | Via <Add> in the Process Participants area, you can define which organizational units from the organizational chart perform this task. The Process participants table in the details of a task should only be used in exceptional cases. To determine which organizational units are responsible for performing a task, use swimlanes. |
Used in process | The 'Used in process' area shows the different processes in which this task was modeled (see Reusing & copying objects) |
Numbering of tasks
A number can be assigned in the details of tasks and sub-processes. The tasks and sub-processes are sorted in ascending order in the list Actions of the process details and in the process description according to the numbering.
The number is a text field, so letter/number combinations can also be used for numbering. There are 2 numbering options:
Manual numbering in the task details | To do this, open the properties of each task and enter a number via <Edit details>. SmartProcess sorts numbering by the leading digit only. Therefore it is recommended to use a 'leading zero' to ensure that tasks are sorted correctly, that is, '01' instead of '1'. |
Numbering mode in the Process designer  | By clicking on the <No.> button in the formatting bar of the Process designer, a list of all activities in the process model opens on the right-hand side of the screen. 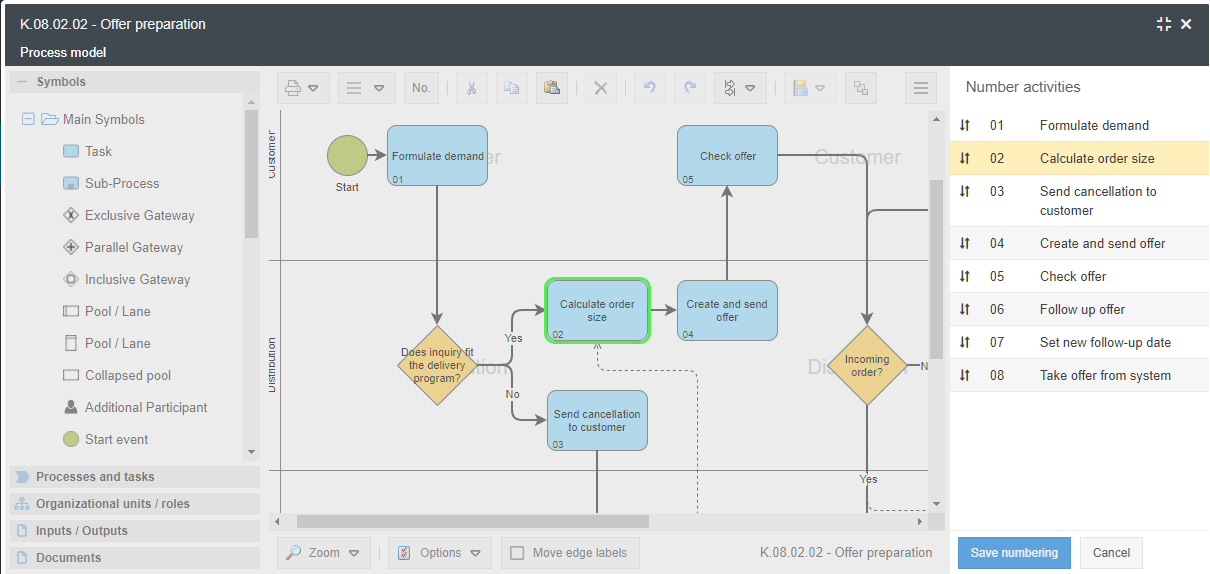 You can now drag and drop the tasks into the desired order. The currently selected task will be highlighted in the process model. You can accept the new numbering with <Save numbering> or discard it with <Cancel> and return to the previous state. The numbering made here can subsequently be overwritten again at any time via the manual numbering of the tasks. |
Task Types
By right-clicking on the task in the process model, you can optionally select a task type to specify the kind of the task.
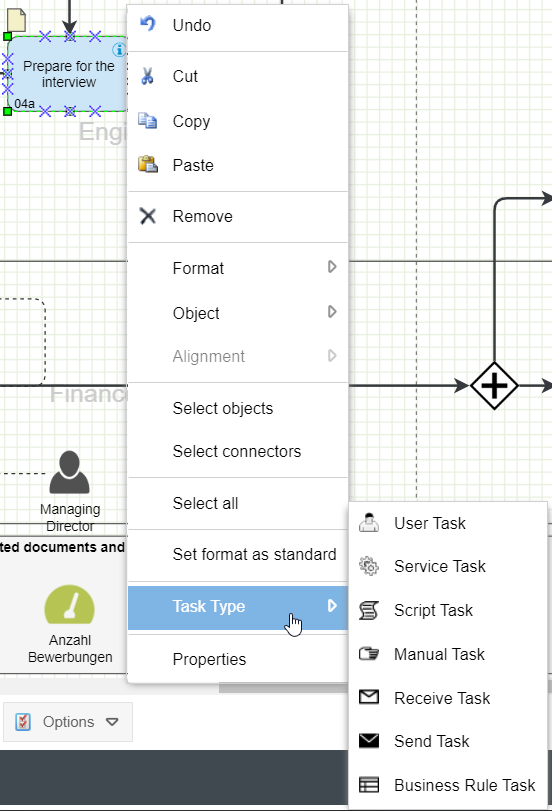
Available for selection:
User Task | Marks a task that a person performs manually after being requested to do so by an IT system. For example: An employee is prompted by the ERP system at the beginning of the month to enter a key figure and then enters the current value into the system. |
Service Task | Marks a task where service tasks are performed by automated applications or web services. |
Script Task | Marks a task that can be executed directly by the Business Process Engine. |
Manual Task | Marks a task that a person performs manually after being manually requested to do so by another person. For example: An employee receives a request from a colleague by telephone to search for documents from the archive. |
Receive Task | Marks a task that only starts when a message is received from a third person. Example: The task "Process request" can only be executed after a customer has sent a request via e-mail. |
Send Task | Marks a task that ends with a message being sent to a third person. For example: The task "Create offer" ends with the offer being sent to a prospect via e-mail. |
Business Rule Task | Marks a task to which a business rule is applied. For example: The determination of the discount for a customer depending on the duration, running costs and the order amount. |
Activity marker
Right-click on the task to specify whether and how a task is performed repeatedly.
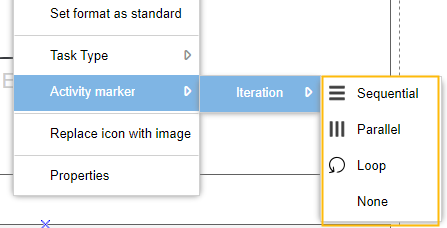
Sequential | A task that is repeated as many times as the given situation requires. Executions are done one by one and the amount of repetitions can be determined right at the beginning.
|
Parallel | A task that is repeated as many times as the given situation requires. Executions are all done in parallel and the amount of repetitions can be determined right at the beginning.
|
Loop | A task that is performed repeatedly until a defined goal is achieved. Performances occur one at a time and the amount of repetition is not predictable at the beginning.
|
None | A task that is performed once. |
How did we do?
Overview: BPMN objects
Object: Sub-Process
