Login & Startpage
Login and password
Structure of SmartProcess
Customize start page
Elements on the start page
Customize main menu
Full text search
Workflows and Cases
Create Workflows
Workflow objects
Workflow object: Task
Workflow object: Decision
Workflow object: Forward case
Workflow object: Send e-mail
Workflow object: Start, intermediate and end event
Workflow object: Timer
Workflow object: Parallel gateway
Workflow object: Sub-Process
Workflow object: Incoming message
Workflow object: Send form via e-mail
Workflow object: Service/Export
Form designer
Form fields
General field properties
Field: Text / List without multiple selection
Field: Multiple selection list
Field: Multirow text
Field: Multirow formatable text
Field: Number
Field: Date
Field: Date / Time
Field: Function-Fied
Field: Contact selection
Field: Field group
Field: Catalog fields
Field: Data source for processes and documents
Field: Process and Document fields
Field: Wiki
Field: Free input
The form designer
Workflow basics
Process model of a workflow
Workflow Settings
Rights workflow participants
General placeholders for Word reports in workflows
Case processing
Workflow-Applications
Processes
Menu structure & terms
Process modelling
Process objects
Overview: BPMN objects
Object: Task
Object: Sub-Process
Object: Connectors
Object: Events
Object: Gateways
Object: Pool & Swimlane
Object: Artifacts in general
Object: Artifacts IT System, Resource
Object: Data object Input / Output, Adjacent process
Object: Artifacts KPI, Risk, Control, Opportunity
Object: Artifact Related document
Additional modelling objects
User-defined images as modeling objects
The process designer
Create process groups & processes
Formatting and positioning objects
Reuse & copy objects
Process details
List: Details
User-defined fields
List: Actions
List: Documents
Lists: Terms and abbreviations / Requirements
Lists: Indicator (KPI), Risks, Opportunities
List: Process participants
Process description
Publication and access rights
State and version
Publication of processes / documents
Validity
Read and edit access
Read confirmation
Knowledge questions for read confirmation
Additional features for processes
Documents
Documents - menu structure
Create documents
Document details
Edit files directly in Office
Properties and Placeholders in Word files
Documents - State, version, publication and validity
Organization chart
Reporting
Reporting menu
Reporting for processes and documents
Reporting for cases
Saved reports
Share reports
Excel Report Designer (Additional module)
Catalogs
Settings
Users, permissions & organizational units
Authorization profiles
Introduction authorization profiles
Authorization profile - Tab Workflows / Cases
Authorization profile - Tab Processes
Authorization profile - Tab Documents
Authorization profile - Tab Organization chart
Authorization profile - Tab Reporting
Authorization profile - Tab Contact
Authorization profile - Tab User
Authorization profile - Tab Catalogs
Authorization profile - Tab Wiki
Authorization profile - Tab Administration
Authorization profile - Tab Others
Organizational units and roles
Manage users
Representative
Catalogs
Import
Import of data
Contact import
User import
Organizational unit import
Case import
Meta data import for documents
Emails and text modules
Configure application
Language
Automatic translation
Date and time
Login options and views
Settings for process management
Modeling rules
Symbols for processes and process groups
Process view
Settings for document management
Document templates
Document type
Settings for the organizational chart
Display of the logos
Unavailability for cases for dates
Directory services (AD, Entra ID / Azure AD) and single sign-on
User notifications
Password security
IP Filter (only for SaaS Systems)
API Profile (Additional module)
Manage maintenance access (only for SaaS systems)
Word report designer for printouts (Additional module)
AI Function SmartAI (Additional module)
Audit Trail
Initial configuration SmartProcess - Process and document management
Video tutorials
Video tutorials: Business Process Management
Video tutorial for process participants
Video tutorial for working with workflow cases
Video tutorial on audit management
Version & Release notes
Release Notes
Version 24.9 Release Notes
Version 23.10 Release Notes
Version 22.10 Release Notes
Version 22.5 Release Notes
Version 22.3 Release Notes
Version 21.3 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.10 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.9 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.8 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.7 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.6 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.5 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.4 Release Notes
Version 9.1.0.3 Release Notes
Manuals from previous versions
Version 25.11 Release Notes
Version 25.3 Release Notes
Info about version
General
SmartProcess API
Mobile Web App
HTML field
Contacts
File attachments in SmartProcess
Manage Wikis
Use QR codes with SmartProcess
Contact & Forum
Language
You can manage the different languages used in the system in the Language menu item. These languages are available for all users to choose from after logging in. Which language is used for the first…
You can manage the different languages used in the system in the Language menu item. These languages are available for all users to choose from after logging in. Which language is used for the first login and for the e-mail sent previously with the login data can be defined by the administration when creating each user.
The difference between system language and content language
System language (green in the image) refers to language packages that are provided by CWA as standard (German and English) or can be purchased additionally. They include the entire user interface (UI), e.g. buttons, menu items or settings, and are only expanded through support.
Content languages (yellow in the image), on the other hand, refer to all content created by users themselves, such as process names, task descriptions or wiki articles. They can be freely added to this menu at any time.
By adding a new content language, a task can also be described in Italian without having to acquire a system language. If users now change the language in the application header to Italian, the correspondingly translated content is displayed in the Italian version, while the user interface continues to be displayed in one of the system languages. Which one this is depends on the order here in the menu: The system language that is further up is used.
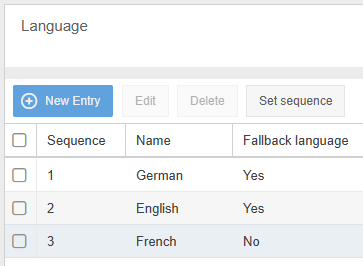
Fallback language
The fallback language is used to control whether content fields that have not been translated are displayed empty when called up or whether the specified fallback language is used instead. Several fallback languages can be defined so that they can replace each other.
How did we do?
Automatic translation
